Information Utilities
What are Information Utilities?
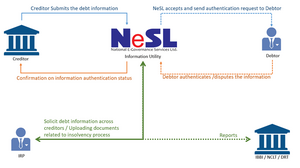
An Information Utility (IU) is an entity registered under Section 3(21) of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (IBC), established to collect, store, authenticate, and provide access to financial information in a standardised and secure manner.[1] It serves as a centralised depository that maintains records of debt, liabilities, defaults, and security interests of persons or entities. The purpose of an Information Utility is to ensure the availability of reliable financial data to stakeholders, reduce disputes regarding default, and facilitate efficient insolvency and bankruptcy resolution processes.[2]
Official Definition of Information Utility
As defined in Legislation
IBC 2016
Section 3(21) of IBC formally defines information utility as a person who is registered with the Board as an information utility[1] under section 210 of IBC.[3] In other words, an IU is a company that has obtained a certificate of registration from the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) to function as an information utility in accordance with Chapter V of the Code (Sections 209-216).[4]
Registration of IUs
An application for registration must be submitted to the IBBI in the prescribed form and manner, including all required details and the applicable fee as specified by the relevant regulations. If the IBBI is satisfied that the application meets all the necessary criteria, it may issue a certificate of registration to the applicant.[5]
Eligibility for Registration
Only a public company can be registered as an information utility whose sole object would be to provide core services and other services under Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, and discharge such functions as may be necessary for providing these services. Its shareholding and governance should be in accordance with Chapter III of IBC, its bye-laws in accordance with Chapter IV of IBC, and has a minimum net worth of fifty crore rupees. The person itself, its promoters, its directors, its key managerial personnel, and persons shall hold more than 5%, directly or indirectly, of its paid-up equity share capital or its total voting power, are fit and proper persons.[6] As of 26 November 2025, there is only one company registered as IU i.e., National E‑Governance Services Limited (NeSL).[7]
Application for Registration or Renewal
A person eligible for registration as an information utility may make an application to the Board in Form A of the Schedule, along with a non-refundable application fee of five lakh rupees. An information utility seeking renewal of registration shall, at least six months before the expiry of its registration, make an application for renewal in Form A of the Schedule, along with a non-refundable application fee of five lakh rupees. The Board shall acknowledge an application made under this Regulation within seven days of its receipt.[8]
Conditions for Registration
The certificate of registration remains valid for five years from the date of issue. During this period, the information utility must comply with IBC and its own bye-laws, continue to meet the eligibility requirements prescribed under Regulation 5(4), pay a registration or renewal fee of ₹50 lakh to the IBBI within fifteen days of receiving the registration or renewal notice, and also pay an annual fee of ₹50 lakh within fifteen days from the commencement of each financial year.[9]
Regulation of IUs
Regulatory requirements to be complied by Information Utility
Access of data
If the adjudicating authority is required to access data from the IU, it should be made available to it immediately and free of charge. The IU must ensure that the adjudicating authority is only provided with the data relevant to the case being heard by the adjudicating authority.[10]
Indemnification
The IU is responsible for performance of its core services under the Act, rules and regulations. As long as an IU authenticates the data it receives and stores it according to specified requirements, it cannot be held liable for the accuracy of the data stored therein. However, if loss is caused by negligence on the part of the IU in performing its services to the debtor or creditor, the IU should be liable to indemnify the debtor or creditor.[11]
Exit Management Plan
Because the information stored in an IU is of regulatory interest, even if the IU is about to fail or its registration is about to be cancelled, the information must remain available to the market. Each IU shall prepare an exit management plan when applying for certification of registration. This plan will contain details on how the regulator can retrieve the data in the IU and transfer it to another IU chosen by the regulator.[12]
Grievance Redressal
Every IU must have a grievance-redressal policy to address consumer grievances. The IU should also report the number of grievances received and resolved periodically to the regulator.[13]
Outsourcing of Core Services
The IU shall not outsource the provision of its core services to a third-party service provider.[14]
Obligations of IUs
An IU must create and store financial data in a universally format accessible to everyone. It should accept electronic submissions of financial info from those required or willing to submit it, following regulatory guidelines. The IU must ensure high service quality standards and get the submitted information authenticated by all relevant parties before storing it. It provides access to this data to anyone authorised to see it, publishes certain statistics as required by the regulations, and connects seamlessly with other IUs to share information. This means the IU acts as a secure, reliable digital platform that collects, verifies, stores, and shares important financial information while ensuring transparency and interoperability within the insolvency framework.[15]
An IU must set up a strong risk management system following technical standards. This system should ensure their services are reliable, secure, and can be recovered easily. The IU must also have plans to keep services running during disasters or emergencies, including backup sites to maintain business continuity.[15]
An important standard used by the IU industry is a common Application Programming Interface (API) whereby all IUs interact with other stakeholders in the performance of their core services. This API specifies how an IU can be inquired for information, how information can be submitted to an IU, how it can be authenticated, how it can be retrieved and how IU prices can be queried.
Duties of IUs
An Information Utility must:
- Provide services carefully and skillfully,[16]
- Keep information safe and act as its custodian,[17]
- Offer services fairly to everyone,[18]
- Only provide services with the user’s clear consent,[19]
- Protect users’ rights,[20]
- Have strong procedures to prevent loss or damage to records,[21]
- Use secure systems for handling information,[22]
- Guard against unauthorized access or misuse of data,[23]
- Transfer information to another IU if the user requests it.[24]
An IU must not:
- Outsource its core services,[25]
- Use stored information for purposes other than those allowed without IBBI’s permission,[26]
- Ask for user data beyond what is necessary for its services.[27]
Services of IUs
The role of IUs in corporate insolvency depends on three key factors: the presence of debt and default information in the IU, the acceptance of that information as valid evidence in court, and how this information is used in the insolvency process. When insolvency proceedings are triggered, defaults recorded in the IU are used by the adjudicating authority to start the process. Additionally, IU data is crucial during the formation of the creditors’ committee, as it helps identify all creditors of the debtor efficiently.[28]
Bye-Laws of IUs
An information utility, for the conduct of its operations, shall have bye-laws consistent with the Code. The bye-laws shall be consistent with, and provide for all matters contained in the Technical Standards. The bye-laws shall provide for the manner and process of providing core services and other services under these Regulations; risk management; rights of users; and grievance redressal.[29]
Statutory Basis of Information Utilities
National e-Governance Services Ltd. (NeSL) is India’s first Information Utility and is registered with the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) under the aegis of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (IBC). It was incorporated on 24 June 2016 as a Union Government Company. There are ongoing efforts to integrate IUs with other digital systems such as MCA-21 and CERSAI to speed up default authentication and create a seamless, end-to-end digital insolvency process. The government is also working on an Integrated-Tech Platform to connect stakeholders like IBBI, lenders, and tribunals, leveraging automation to streamline insolvency procedures and enhance efficiency. IBBI has issued stricter guidelines to enhance identity verification and authentication processes, ensuring more accurate and verifiable financial information, which reduces disputes in insolvency resolution.[30]
As defined in Official Government Reports
As per an information brochure released by IBBI, an IU is required to maintain electronic database of information and provide authentic information to eliminate delays and disputes relating to claims and defaults. It is mandated to provide core services, such as acceptance of electronic submission of financial information; safe and accurate recording of financial information; authentication and verification of financial information; and providing access to information stored with them to specified persons. An IU is required to provide core services in respect of financial information, which include records of the debt of a person, liabilities when a person is solvent, assets of a person over which security interest has been created, instances of default by a person against any debt, the balance sheet and cash-flow statements of a person.[2]
Bankruptcy Law Reforms Committee
The Bankruptcy Law Reforms Committee (BLRC) emphasised the importance of establishing an "information infrastructure" to strengthen the insolvency and bankruptcy resolution framework. It noted that the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) often needs to determine both facts and law, which can delay the process of assessing a debtor's viability. The BLRC recommended minimising factual disputes by digitising credit transactions and storing them on a secure digital platform with legal validity. These authenticated electronic records would help quickly identify creditors, form the committee of creditors upon default, and assess the debtor’s viability efficiently. To achieve this, the BLRC proposed setting up a regulated Information Utility (IU) to bridge information gaps, ensure transparency, and support timely resolution of insolvency and bankruptcy cases.[31]
IBBI - Working Group Committee report (2017)
In the report of the working group on information utilities, the working group (WG) noted that " IUs are a novel concept. While there are many entities all over the world that store information about credit, there are no exact equivalents of IUs. Therefore, while establishing this new kind of entities, it is important to have a clear idea of the services that IUs shall provide, and the processes through which they shall do so. The primary function that IUs perform, that make them important from a public policy point of view, is that they provide high-quality authenticated information about debts and defaults."[32]
IBBI - Technical Committee Report
The "Report of the Technical Committee on Information Utilities" (August 2017) by the IBBI sets out the technical standards for IUs under the IBBI Regulations, 2017. The report covers key aspects such as user registration and identification primarily through Aadhaar or PAN, unique identifiers for users and debts, secure digital submission of data, and frameworks for authentication and consent. The report also addresses stringent data integrity and security measures, requiring business continuity plans, disaster recovery protocols, encryption, and regular security audits. Risk management frameworks are prescribed to identify, assess, and mitigate operational and IT risks, with clear roles and mandatory reporting to the regulator. Data preservation standards ensure all records and digital signatures are retained in original form for up to eight years, allowing interoperability among IUs while maintaining confidentiality and compliance.[33]
As defined in Case Laws
The Supreme Court held that the adjudicating authority must only look at the IU record or other evidence produced by the financial creditor to ascertain default under IBC and focused on the evidentiary weight that IU records carry in insolvency proceedings.[34]
In Swiss Ribbons Pvt. Ltd. vs Union of India & Ors., the information utility is defined as not only collecting financial data, but also checks whether a default has occurred or not.[35]
The Supreme Court, in Vijay Kumar Singhania vs Bank of Baroda (August 29, 2024), held that a financial creditor is not limited to submitting only the default record from an IU, they can also submit other specified evidence of default as allowed under the CIRP Regulations.[36]
Tech transformation
Status of Digitisation
NeSL is the first and only IU currently operational, serving as a centralized digital repository for debt and default records. It was set up by leading public-institutions like State Bank of India, Life Insurance Corporation of India, Canara Bank, Bank of Baroda, ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank and Axis Bank. The primary role of NeSL is to serve as a repository of legal evidence holding the information pertaining to any debt/claim, as submitted by the financial or operational creditor and verified and authenticated by the parties to the debt.[37]
Digital Document Execution
It is a platform used where the debtor and the creditor jointly execute a document, requiring both parties to upload documents. DDE is a mode for paperless execution and storage of financial contracts, which will result in superior enforcement, thereby enhancing the ‘Ease of Doing Business’ especially in times where quick financing is the need of the hour for businesses.[38]
Functionality and Process
- The execution of the document via DDE must adhere to the provisions of the respective Stamp Act.
- Arrangements have been made with various State Governments to facilitate the online and real-time payment of stamp duty.
- The platform supports three types of signatures for authentication: Aadhaar-based OTP e-sign, dongle-based e-sign digital signature certificate (DSC), and biometric-based e-sign authentication.
- NeSL's DDE facility offers a wider reach compared to the use of dongle-based DSC, which is not generally available to all.
- To benefit underprivileged segments that may lack a permanent dwelling or an Aadhaar-linked mobile phone, NeSL introduced a biometric mode of authentication that captures fingerprints and verifies them against the Aadhaar database.
- The data related to digitally executed documents can be analyzed and subjected to data mining.[39]
Adoption and Benefits
- NeSL’s DDE has become increasingly popular, with more than 11 million transactions completed.
- DDE is increasingly viewed as a universal contracting solution.
- It provides significant advantages by saving time and costs associated with documentation.
- By eliminating the need for physical travel or office visits, DDE reduces costs and risks, and the process is environment friendly.[40]


As of August 20, 2025, the NeSL has reached 28.37 lakh unique registered users and currently stores a total of 470.71 lakh debt records, both standard and default. The cumulative debt amount tracked on the platform stands at ₹329.56 lakh crores, with 18.99 lakh records classified as defaults, accounting for ₹27.41 lakh crores in defaulted debt. These statistics demonstrate the scale and active digitisation of debt information exchange within India’s insolvency and financial framework.[41]
Appearances in Official Databases
Government Database
There is currently only one IU in India which is NeSL.
The NeSL dashboard functions as a structured financial information database maintained by an Information Utility under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016. The dashboard does not merely display documents; it organises financial relationships into standardised, searchable data fields that together constitute Digital Debt Evidence.
NeSL Home Page
This is the general NeSL portal where dashboard login and IU services are discussed, useful for accessing logged-in dashboards directly.
NeSL Submission of Financial Data / Data Fields
This page relates to how financial information (including debt details) is submitted to NeSL, and implicitly indicates required fields (such as date of disbursement, currency, etc.). This is where one can see examples of specific fields that the backend database/dashboard would store (e.g., date of disbursement, currency of debt, etc.).
NeSL Record of Default (RoD) Page
This page is the official NeSL interface for recording and viewing default information — the key category of data that the dashboard displays. This page shows the IU function that directly maps to the default information fields on the dashboard.
NeSL Bye-Laws
This document contains governance definitions including unique identifiers for users and debts, which underlie the data fields that would appear on the dashboard (UDI, UIN, default details, etc.)

Research the engages with Information Utilities
"Law and economics approach to information asymmetry in insolvency resolutions: enhancing creditor confidence and resolution outcomes under India’s IBC framework", Emerald Insight
The paper “Law and economics approach to information asymmetry in insolvency resolutions: Enhancing creditor confidence and resolution outcomes under India’s IBC framework” (Thakkar, Maurya, & Sood, 2025) examines how inadequate information availability to creditors under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (IBC) contributes to suboptimal decisions and a high rate of liquidations over resolutions. Using a law-and-economics lens combined with empirical analysis of 196 CIRP cases and stakeholder surveys, the authors argue that information asymmetry erodes creditor confidence, leading them to undervalue viable resolution options. The study highlights the potential of Information Utilities (IUs) as institutional mechanisms to mitigate this asymmetry by aggregating, verifying, and disseminating debtor data, thereby fostering transparency and trust. It recommends strengthening Section 215 of the IBC to make disclosures to IUs mandatory and operational, contending that improved information flow will enhance creditor decision-making, reduce liquidation rates, and better realize the IBC’s goal of value maximization and business continuity.[42]
"A Maximalist Approach to Data Under IBC", Springer Nature Link
Chapter 5, “A Maximalist Approach to Data Under IBC” by Adam Feibelman and Renuka Sane, argues that India’s Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) can achieve its objectives of timely, transparent, and value-maximising resolution only through a comprehensive, data-driven framework. The author advocates a “maximalist” approach—systematic collection, integration, and utilisation of all relevant financial, procedural, and institutional data across tribunals, insolvency professionals, creditors, and regulators—subject to institutional capacity limits. Such a data ecosystem, they contend, would reduce information asymmetry, enable performance analytics, and strengthen stakeholder confidence, while supporting policy refinement and monitoring of outcomes. One of the key institutional actors identified for data collection in IBC ecosystem is the concept of an information utility (IU) — the chapter situates IUs among the “institutions and repeat professional actors within the system” whose functioning and data‐outputs should also be monitored.[43]
“Addressing Challenges of Information Asymmetry in Financial Sector Using Information Utility”, Informit
The paper examines how Information Utilities (IUs), particularly the National E-Governance Services Limited (NeSL), have addressed information asymmetry in India’s financial sector following the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016, by serving as digital repositories of verified financial data that promote transparency and facilitate quicker and fairer insolvency resolution processes; while the IU framework has contributed to improved trust, efficiency, and accessibility in credit markets, ongoing challenges remain—such as issues around shareholding concentration among banks, trust deficits among stakeholders, lack of clarity in data handling, and the need for robust technological safeguards—with the article ultimately concluding that, despite teething problems, the IU system stands as a pioneering model for promoting information symmetry and discipline within the Indian credit ecosystem, and offers lessons for similar reforms globally.[44]
"Information Utilities and Blockchain: An Unlikely but Holy Partnership", IBBI
The IBBI research paper titled “Information Utilities and Blockchain: An Unlikely but Holy Partnership” by Ankeeta Gupta explores the concept, challenges, and future potential of Information Utilities (IUs) under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 in India. It notes that IUs are envisaged to create financial information symmetry among creditors and debtors by collecting, collating, authenticating, and disseminating financial data to support faster and more transparent insolvency resolution. Currently, India has only one registered IU, National E-Governance Services Ltd (NeSL), which has faced challenges establishing trust and broad stakeholder acceptance. To overcome these, the paper proposes integrating blockchain technology with IUs to ensure immutable, transparent, secure, and readily accessible financial records. Blockchain’s decentralized ledger and cryptographic security features could resolve trust deficit issues and enhance data authenticity and transparency. The report underscores that this integration could lead to better insolvency outcomes, greater confidence amongst stakeholders, and set a pioneering global example. The study combines doctrinal and empirical research, including interviews with insolvency professionals in India, highlighting the nascent but promising progress of IUs and the disruptive potential of blockchain in insolvency data management.[45]
Data Challenges
IU filing is still not the sole route to prove default, benches have treated IU records as directory rather than mandatory. This weakens incentives to file systematically and creates patchy coverage across creditor classes ( banks vs NBFCs vs Operational creditors).[46] User onboarding and debtor-side authentication have been pain points; inconsistent KYC/ID mapping (PAN/CIN/LEI) across institutions degrades match quality between legal entities and loan records. (Recent IBBI changes try to harden user authentication via UIDAI demographic checks, but roll-out and interoperability remain practical hurdles.)[47] Key datasets relevant to default—CERSAI charge filings, MCA charge data, credit bureau histories, DDE/e-stamping metadata—are not natively harmonised/API-fied with the IU, forcing duplicative filing and manual reconciliation. Policy notes repeatedly flag the need for an integrated IT spine across IBBI/NCLT/NeSL and allied registries.[48]
Way Ahead
The way ahead for Information Utilities (IUs) involves standardisation and harmonisation of available data.[49] It is recommended to establish uniform data formats and reporting standards across all creditors and IUs, ensuring seamless integration and consistency. Build on IBBI technical standards by prescribing uniform frameworks (core mandatory fields, controlled vocabularies for security/charge type, standard borrower IDs like CIN/PAN/LEI) and validator rules across lenders, so submissions are analytics-grade on day one.[50] Improving data collection in the future requires mandating verified record submissions from both financial and operational creditors, alongside automated notification and reminder systems to ensure timely debtor authentication.[51] Adoption of transparent and technologically advanced methods, such as blockchain for secure records, is also suggested to boost trust and efficacy of IUs.[52] These measures collectively aim to streamline insolvency processes, reduce delays, and foster confidence among stakeholders in the insolvency ecosystem.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016, § 3(21), No. 31 of 2016, Acts of Parliament, 2016 (India).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, reg. 30(2)(c).
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016, § 210, No. 31 of 2016, Acts of Parliament, 2016 (India).
- ↑ The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016, Chapter V—Information Utilities (Sections 209 to 216).
- ↑ IBC, § 210 in conformity with Regulation. 6, IBBI (Information Utility) Regulations, 2017.
- ↑ IBBI (Information Utility) Regulations, 2017, Regulation 3.
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India. “Information Utilities (IUs)”. IBBI — Service Providers. https://ibbi.gov.in/en/service-provider/information-utilities
- ↑ IBBI (Information Utility) Regulations, 2017, Regulation 4.
- ↑ IBBI (Information Utility) Regulations, 2017, Regulation 6.
- ↑ IBBI (Information Utility) Regulations, 2017, Regulation 23(3).
- ↑ IBBI (Information Utility) Regulations, 2017, Regulation 31.
- ↑ IBBI (Information Utility) Regulations, 2017, Regulation 39.
- ↑ IBBI (Information Utility) Regulations, 2017, Regulation 12.
- ↑ IBBI (Information Utility) Regulations, 2017, Regulation 30(2)(a).
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016, § 214, No. 31 of 2016, Acts of Parliament, 2016 (India).
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, reg. 28(1).
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, reg. 28(2).
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, reg. 29.
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, reg. 30(1)(a).
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, reg. 30(1)(b).
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, reg. 30(1)(c).
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, reg. 30(1)(d).
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, reg. 30(1)(e).
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, reg. 30(2)(c).
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, reg. 30(2)(a).
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, reg. 30(2)(b).
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, reg. 30(2)(c).
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India, Information Utilities: A Key Pillar of Insolvency Proceedings (Information Brochure, IBBI, updated 30 November 2020) https://ibbi.gov.in/uploads/publication/ee64e0a0330c81c11c0ab538b5e4b946.pdf
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017, reg. 15.
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India. IBBI – Building a Resilient Economy. New Delhi: IBBI, 2024. Available at: https://ibbi.gov.in/uploads/whatsnew/c0915e0d5951aa810e4c9bd240a0b76d.pdf
- ↑ Bankruptcy Law Reforms Committee, The Report of the Bankruptcy Law Reforms Committee: Volume I—Rationale and Design, Government of India, Ministry of Finance, November 2015, available at https://ibbi.gov.in/uploads/resources/BLRCReportVol1_04112015.pdf
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India, Report of the Working Group on Information Utilities (WG-04), January 2017.
- ↑ Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India, Report of the Technical Committee on Information Utilities, August 2017, available at https://ibbi.gov.in/uploads/resources/Report_of_the_Technical_Committee_on_Information_Utilities2.pdf.
- ↑ Innoventive Industries Ltd. vs. ICICI Bank & Anr., Civil Appeal Nos. 8337-8338 of 2017, Supreme Court of India, 2017, available at ibbi.gov.in/webadmin/pdf/order/2017/Sep/31%20Aug%202017%20in%20the%20matter%20of%20Innoventive%20Industries%20Ltd.%20Vs.%20ICICI%20Bank%20&%20Anr.%20Civil%20Appeal%20Nos.8337-8338%20of%202017_2017-09-01%2009:56:52.pdf
- ↑ Swiss Ribbons Pvt. Ltd. & Anr. v. Union of India & Ors., Writ Petition (Civil) No. 99 of 2018 (along with Writ Petitions (Civil) Nos. 100/2018, 115/2018, 459/2018, 598/2018, 775/2018, 822/2018, 849/2018 & 1221/2018; Special Leave Petition (Civil) No. 28623 of 2018) (Supreme Court of India, 25 Jan. 2019).
- ↑ Supreme Court in Civil Appeal (Diary No.) 5768 of 2024
- ↑ American Express. What is National E-Governance Services Limited (NeSL) Reporting. Available at: https://www.americanexpress.com/in/customer-service/faq.what-is-national-egovernance-services-limited-reporting.html
- ↑ Batra, S. (n.d.). Corporate insolvency: The road to Viksit Bharat (2nd ed.). EBC Page No. 251-253
- ↑ Batra, S. (n.d.). Corporate insolvency: The road to Viksit Bharat (2nd ed.). EBC Page No. 251-253
- ↑ Batra, S. (n.d.). Corporate insolvency: The road to Viksit Bharat (2nd ed.). EBC Page No. 251-253
- ↑ National e-Governance Services Ltd. (2025). NeSL official website. Retrieved November 8, 2025, from https://nesl.co.in/
- ↑ Thakkar, Hiteshkumar, Maurya, Khyati, and Sood, Saransh. “Law and economics approach to information asymmetry in insolvency resolutions: Enhancing creditor confidence and resolution outcomes under India’s IBC framework.” International Journal of Law and Management (2025). Emerald Insight. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJLMA-02-2025-0054
- ↑ Feibelman, A., Sane, R. (2022). A Maximalist Approach to Data Under IBC. In: Thomas, S. (eds) Insolvency and Bankruptcy Reforms in India. India Studies in Business and Economics. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0854-4_5
- ↑ Gupta, Ankeeta. “Addressing Challenges of Information Asymmetry in Financial Sector Using Information Utility.” Informit. https://search.informit.org/doi/abs/10.3316/informit.024807763962106
- ↑ Gupta, Ankeeta. (2022). Information Utilities and Blockchain: An Unlikely but Holy Partnership. Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India, Research Division. Retrieved November 8, 2025, from https://www.ibbi.gov.in/uploads/publication/6b683482bf24ca7023aa99c8ef198bd8.pdf
- ↑ LiveLaw. (n.d.). Information to NeSL/Information Utility not mandatory for ascertainment of default: NCLT Mumbai. https://www.livelaw.in/ibc-cases/information-to-neslinformation-utility-not-mandatory-for-ascertainment-of-default-nclt-mumbai-286924
- ↑ Business Standard. (2025). IBBI amends standards for information utilities; rules to enhance verification. https://www.business-standard.com/economy/news/ibbi-amends-standards-for-info-utilities-rules-to-enhance-verification-125013001425_1.html
- ↑ Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs. (2024). IBC Brief Q3 2023–24. Page 1. https://iica.nic.in/images/Report-2024/IBC-Brief-Q3-2023-24.pdf
- ↑ Insolvency: What is important about information utilities? https://www.amsshardul.com/insight/insolvency-what-is-important-about-information-utilities/
- ↑ IBBI. (2017). Standards and guidelines (Final). https://ibbi.gov.in/webadmin/pdf/whatsnew/2017/Dec/FINAL%20STANDARDS%20GUIDELINES%2013.12.2017_2017-12-13%2021:39:59.pdf
- ↑ IBBI. (2017). WG-04 report on information utilities. https://www.ibbi.gov.in/wg-04report.pdf
- ↑ Gupta, Ankeeta. (2022). Information utilities and blockchain: An unlikely but holy partnership. Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India, Research Division. https://www.ibbi.gov.in/uploads/publication/6b683482bf24ca7023aa99c8ef198bd8.pdf
